-
Article
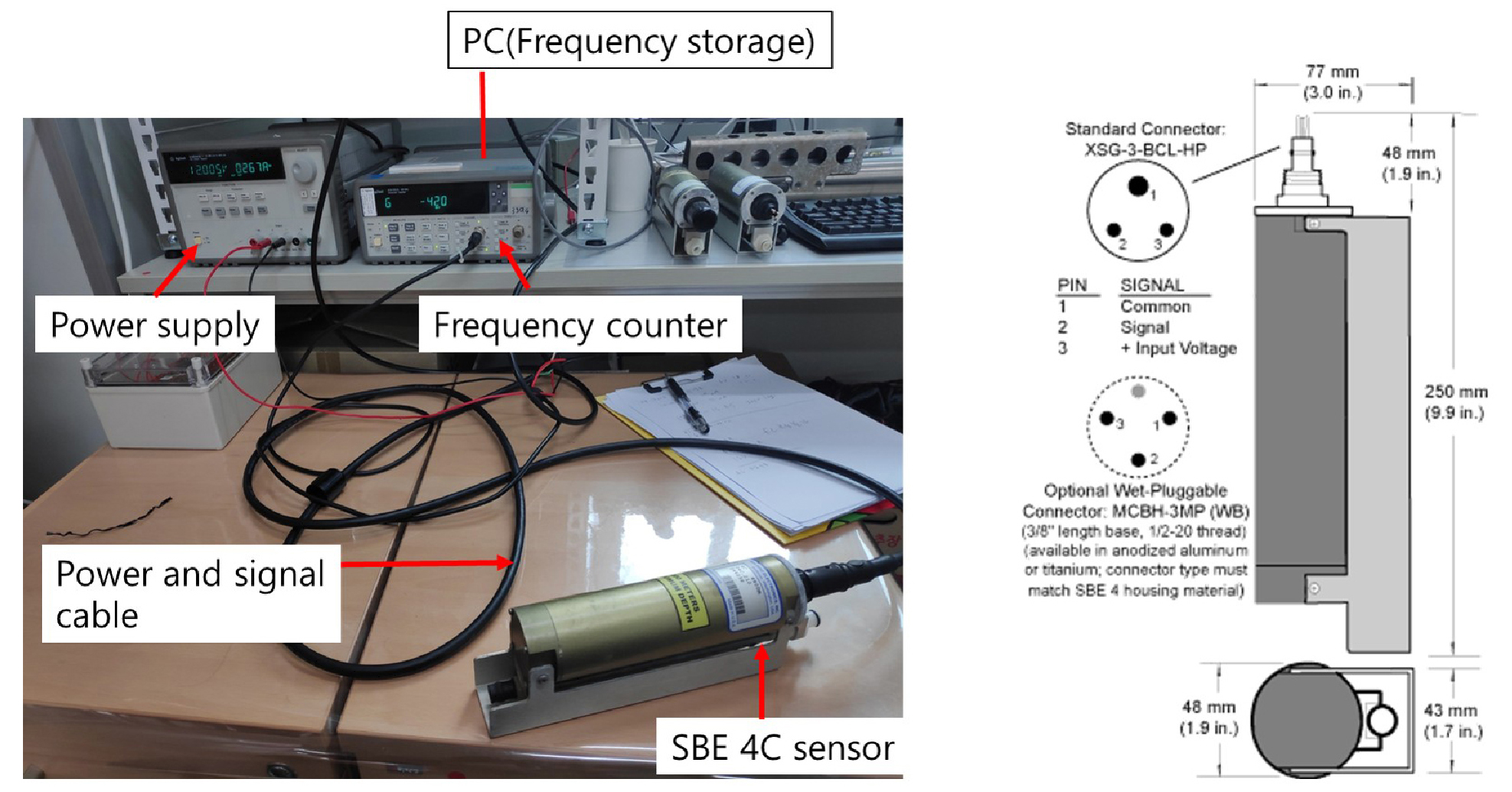
-
Pre-inspection of CTD Salinity Sensor (SBE 4C) and Salinity Data Correction after Observation
CTD 염분 센서 (SBE 4C) 사전 검사 및 관측 후 염분 자료 보정
-
TAEKEUN RHO, SANG DO HEO AND JOONSEONG PARK
노태근, 허상도, 박준성
- Seawater salinity refers to the total amount of dissolved inorganic salts in 1 kg of seawater and provides crucial information for understanding …
해수 염분은 해수 1 kg에 녹아 있는 무기염류의 총량으로 해양 내부 물리 및 화학 특성 변화와 전 지구적 기후에 해양이 미치는 영향을 …
- Seawater salinity refers to the total amount of dissolved inorganic salts in 1 kg of seawater and provides crucial information for understanding changes in the physical and chemical properties of the ocean interior, as well as the ocean’s influence on global climate. In oceanographic studies, salinity is typically measured by immersing conductivity and temperature sensors directly into seawater and calculating salinity from the measured conductivity and temperature values. The SBE 4C conductivity sensor, commonly used for high-resolution vertical salinity observations from research vessels, demonstrates high precision and stability in field conditions. However, changes in its electrical characteristics can cause monthly salinity measurement deviations of up to ±0.0023 psu. To achieve the salinity measurement accuracy of ±0.001 psu recommended by the World Ocean Circulation Expedition (WOCE), observations must be conducted within two weeks of sensor calibration to minimize the effects of electrical drift. In coastal areas where observations are conducted multiple times over short periods, the impact of electrical drift is reduced, but physical changes to the sensor caused by biofouling or oil contamination necessitate frequent calibration. In Korea, there is no calibration facility for the SBE 4C sensor, therefore, the sensor must be sent to the manufacturer, Sea-Bird Electronics, in the United States for the calibration. This process takes approximately two to four months, resulting in frequent use of sensors that have been calibrated more than a month prior or continuous observations without regular calibration. This study presents methods for checking the operational status of sensors when pre- and post-observation calibration is not frequently available, correcting observed values using calibration constants before and after observations that last more than one month, and adjusting processes for salinity data observed with sensor using salinity sample analysis.
- COLLAPSE
해수 염분은 해수 1 kg에 녹아 있는 무기염류의 총량으로 해양 내부 물리 및 화학 특성 변화와 전 지구적 기후에 해양이 미치는 영향을 이해하는 데 중요한 정보를 제공한다. 해양에서 염분 관측은 일반적으로 전기전도도 및 수온 센서를 해수에 직접 넣어 측정된 전기전도도와 수온 값으로 계산한다. 선박에서 고해상도 연직 염분 관측에 주로 사용되는 SBE 4C 센서는 현장 환경에서 높은 정밀도와 안정성을 보이지만, 전기 특성 변화로 월간 최대 ±0.0023 psu의 염분 측정 편차를 일으킨다. 세계해양순환탐사(World Ocean Circulation Expedition, WOCE)가 권장하는 염분 측정 정확도인 ±0.001 psu로 염분을 관측하기 위해서는 센서의 전기 특성 변화 영향을 최소화하기 위해 센서 교정 후 최대 2주 이내로 관측을 수행해야 한다. 또한 연안에서 짧은 기간에 여러 번 관측 하는 경우 센서의 전기 특성 변화에 의한 영향은 적게 받을 수 있으나, 생물 부착 또는 유류등에 의한 영향으로 센서 특성이 물리적으로 변할 수 있어 빈번한 센서 교정이 필수적이다. 그러나 국내에는 SBE 4C 센서 교정을 수행하는 시설이 없어 미국에 있는 센서 제조사인 Sea-Bird electronic에 의뢰해야 하므로 센서 교정에 최소 2개월에서 4개월 정도 걸리기 때문에 교정 후 최소 1개월 이상이 지난 센서를 관측에 사용하거나, 관측 전 주기적인 센서 교정 없이 연속적으로 관측하는 때도 빈번하다. 본 연구에서는 관측 전·후 센서 교정이 어려운 경우 센서의 정상적인 작동 여부를 점검하는 방법, 1개월 이상 관측 할 경우 관측 전·후 센서 교정 상수를 이용한 관측값 보정, 관측 중 채취한 염분 시료 분석값을 이용한 염분 센서 보정 방법에 대해서 실제 관측자료와 함께 제시하였다.
-
Pre-inspection of CTD Salinity Sensor (SBE 4C) and Salinity Data Correction after Observation
-
Article
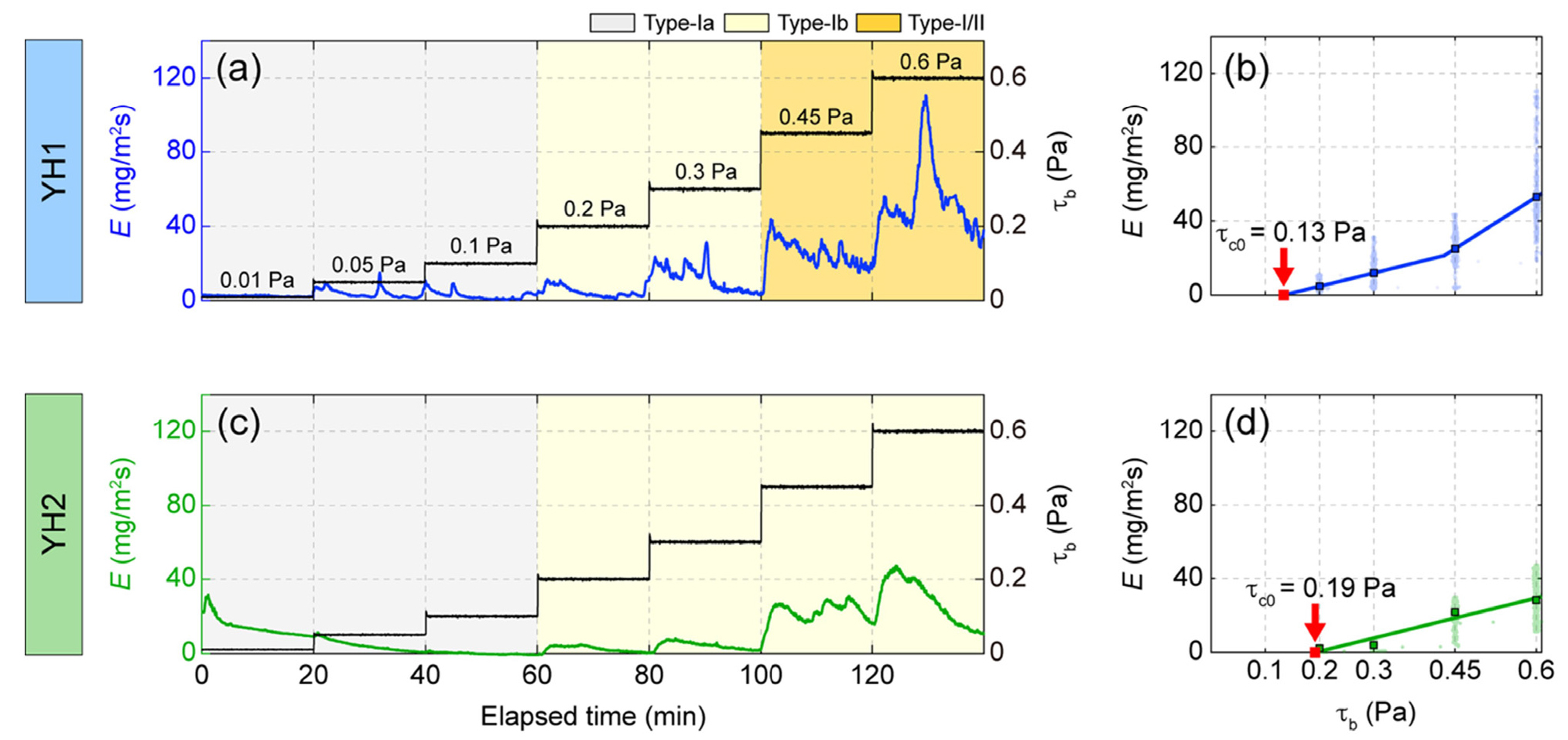
-
Stability of Contaminated Sediments in an Urban Detention Basin: A Case Study from Yonghyeon Tidal Creek, Incheon
도심 유수지 내 오염퇴적물의 안정도: 인천 용현 갯골 사례
-
JAE HYEOK SHIN, WOO JIN LEE, SEONG WOON JEONG, SU IN KIM, CHAE YEON EUN AND HO KYUNG HA
신재혁, 이우진, 정성운, 김수인, 은채연, 하호경
- Detention basins are environments where cohesive sediments readily absorb and settle together with contaminants originating from urban areas. Consequently, understanding sediment erodibility …
유수지는 점착성 퇴적물이 도심으로부터 유입된 오염물질과 함께 흡착되어 침전되기 쉬운 환경이다. 축적된 오염퇴적물의 거동 및 확산을 평가하기 위해서는 퇴적물 안정도를 파악할 필요가 …
- Detention basins are environments where cohesive sediments readily absorb and settle together with contaminants originating from urban areas. Consequently, understanding sediment erodibility is essential to assess the behavior and dispersion of accumulated contaminated sediments. This study collected sediment samples at the inner (YH1) and outer (YH2) parts of Yonghyeon tidal creek (Hagik detention basin) located in Incheon to evaluate sediment stability, and to analyze physicochemical properties and heavy metal concentrations of sediments in order to identify spatial variations. YH1 had finer median particle size (YH1: 22.1 μm, YH2: 31.8 μm) and higher organic matter content (YH1: 10.1%, YH2: 5.1%) than YH2. The sediment erodibility experiment showed a lower initial critical shear stress for erosion (YH1: 0.13 Pa, YH2: 0.19 Pa) and a higher cumulative eroded mass (YH1: 121.3 g/m², YH2: 67.6 g/m²) at YH1 compared to YH2. At YH1, weakened current velocity caused by artificial island and continuous organic matter inputs from the sewage outfall reduced the consolidation of fine-grained sediments, resulting in lower sediment stability. At YH2, intermittent strengthened current velocity during the drainage gate opening led to the dominance of coarse sediments, resulting in higher sediment stability. Furthermore, heavy metal concentrations at YH1 were higher than YH2, with Cu, Ni, and Zn exceeding the NOAA Effect Range-Low thresholds by approximately 1.5, 1.1, and 2 times, respectively. Due to the more cohesive sediments at YH1 compared to YH2, contaminants were more readily absorbed from the sewage outfall and more easily released into the external environment through sediment erosion. Because inflows from the tidal creek can affect water circulation in the adjacent harbor, this study evaluated the erosion mechanisms of contaminated sediments and their potential dispersion by investigating sediment stability and contaminant characteristics within a contaminated urban detention basin.
- COLLAPSE
유수지는 점착성 퇴적물이 도심으로부터 유입된 오염물질과 함께 흡착되어 침전되기 쉬운 환경이다. 축적된 오염퇴적물의 거동 및 확산을 평가하기 위해서는 퇴적물 안정도를 파악할 필요가 있다. 본 연구는 인천광역시에 위치한 용현 갯골(학익유수지)에서 유수지 내측(YH1)과 외측(YH2)의 퇴적물 시료를 획득하여, 퇴적물 안정도를 평가하고, 퇴적물의 물성과 중금속 농도를 분석하여, 공간적 차이를 규명하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 분석 결과, YH1 정점이 YH2 정점보다 중앙입도(YH1: 22.1 μm, YH2: 31.8 μm)가 더 세립하였으며, 유기물 함량(YH1: 10.1%, YH2: 5.1%)이 더 높았다. 퇴적물 침식률 실험 결과, YH1 정점이 YH2 정점보다 최초침식한계전단응력(YH1: 0.13 Pa, YH2: 0.19 Pa)이 더 낮고, 침식된 누적 퇴적물량(YH1: 121.3 g/m2, YH2: 67.6 g/m2)이 더 높았다. YH1 정점은 인공섬의 영향으로 유속이 약하고, 인근 하수관으로부터 지속적인 유기물 유입으로 인해, 세립질 퇴적물의 압밀이 약화되어 퇴적물 안정도가 상대적으로 낮게 나타난 것으로 보인다. YH2 정점은 배수문 개방 시, 간헐적으로 발생하는 강한 유속에 의해 조립질 퇴적물이 더 우세하게 분포하여, 퇴적물 안정도가 높게 나타난 것으로 해석된다. 또한, YH1 정점은 YH2 정점에 비해 중금속 농도가 높았으며, 구리, 니켈, 아연은 각각 NOAA에서 제시한 Effect Range-Low 기준치 대비 약 1.5배, 1.1배, 2배 이상 초과하였다. 이는 YH1 정점의 퇴적물이 YH2 정점보다 점착성이 높아, 인근 도시 하수관으로부터 유입된 오염물질이 상대적으로 잘 흡착되며, 침식에 의해 외부로 쉽게 유출될 수 있음을 보여준다. 갯골에서 유입된 물질은 인근 항만의 해수 순환에 영향을 미칠 수 있으므로, 본 연구는 오염된 도심 유수지에서 퇴적물 안정도와 오염물질 특성에 대한 규명을 통해 오염퇴적물의 침식 기작 및 확산 가능성을 평가하였다.
-
Stability of Contaminated Sediments in an Urban Detention Basin: A Case Study from Yonghyeon Tidal Creek, Incheon
-
Article
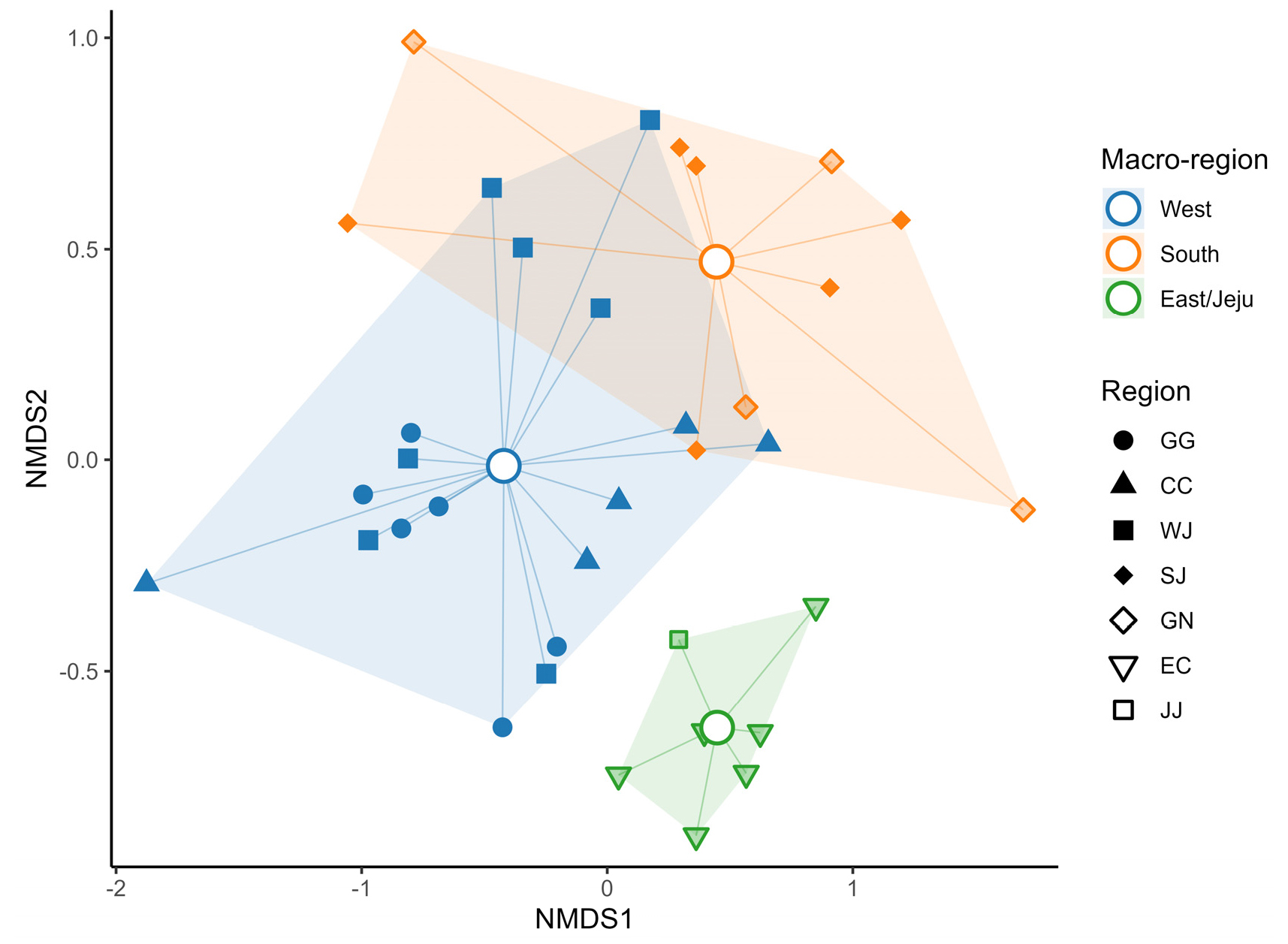
-
Community Structure and Spatial Distribution of Coastal Birds Observed at 35 Major Coastal Wetlands in Korea from 2016 to 2024
2016-2024년 국내 주요 연안습지 35개소에서 관찰된 바닷새 군집 구조 및 공간 분포 특성
-
SEUNG-YEON LEE, SEUNG-WOO HAN, EUN-HONG LIM, SANG-MIN JUNG, DAE HAN CHO, SOON-SIK KIM, HAEJIN CHO, TEHAN KANG, SI-WAN LEE AND HONG-SHIK OH
이승연, 한승우, 임은홍, 정상민, 조대한, 김순식, 조해진, 강태한, 이시완, 오홍식
- Coastal wetlands serve as transitional zones linking terrestrial and marine ecosystems and provide critical habitats for diverse coastal bird species. However, rapid …
연안습지는 육상과 해양을 연결하는 전이지대로서 철새를 포함한 다양한 조류의 핵심 서식지로 기능하지만, 매립·개발·기후변화로 급격히 감소하면서 바닷새 개체군의 국제적 감소가 우려되고 있다. 본 …
- Coastal wetlands serve as transitional zones linking terrestrial and marine ecosystems and provide critical habitats for diverse coastal bird species. However, rapid loss driven by reclamation, development, and climate change has raised global concerns about the decline of coastal bird populations. In this study, we analyzed the community structure and spatial distribution of coastal birds across 35 major coastal wetlands in Korea from 2016 to 2024. A total of 129 species and 579,635 individuals were recorded, with Dunlin Calidris alpina (20.60%) and Black-tailed Gull Larus crassirostris (15.43%) dominant at the species level, and shorebirds (54.30%) and gulls (21.49%) dominant at the taxonomic-group level. Community index patterns revealed strong regional contrasts: the Southern Jeolla region exhibited high species richness, diversity, and evenness with a ‘lognormal-type’ structure, whereas the Jeju region showed a ‘hollow-curve’ pattern driven by a few highly dominant species. NMDS (Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling) and PERMANOVA (Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance) analyses demonstrated clear separation of bird communities among the West, South, and East/Jeju coasts, indicating that habitat characteristics at the regional scale, rather than geographic distance alone, shape community structure. By taxonomic group, shorebirds were concentrated in western tidal flats, dabbling ducks dominated southern estuarine and brackish habitats, and gull assemblages were characteristic of the eastern coast. Additionally, 25 of the 35 survey sites (71.43%) met the Internationally Important Site (IIS) thresholds, with a total of 36 species (22 of which were shorebirds) identified as exceeding global population criteria. These findings highlight the high ecological significance of Korean coastal wetlands within the EAAF (East Asian–Australasian Flyway). The spatial patterns identified in this study underscore the need to incorporate both community- and habitat-level considerations when establishing region- and seascape-scale conservation strategies for coastal bird habitat networks.
- COLLAPSE
연안습지는 육상과 해양을 연결하는 전이지대로서 철새를 포함한 다양한 조류의 핵심 서식지로 기능하지만, 매립·개발·기후변화로 급격히 감소하면서 바닷새 개체군의 국제적 감소가 우려되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 2016–2024년 동안 국내 주요 연안습지 35개소를 대상으로 바닷새의 군집 구조와 공간적 분포 특성을 분석하였다. 총 129종 579,635개체의 바닷새가 관찰되었으며, 종 수준에서는 민물도요(Calidris alpina, 20.60%) 및 괭이갈매기(Larus crassirostris, 15.43%), 분류군 수준에서는 도요·물떼새류(54.30%) 및 갈매기류(21.49%)가 우점하였다. 군집 지표 분석 결과, 전라남부 권역은 종수·다양도·균등도가 모두 높아 lognormal형 구조를 보였으나, 제주는 소수 종의 높은 우점으로 hollow-curve형 구조를 나타냈다. NMDS (Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling) 및 PERMANOVA (Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance) 분석에서는 바닷새 군집이 서해, 남해, 동해/제주로 뚜렷하게 분리되어, 지리적 거리보다는 권역별 서식지 특성이 군집 구조를 규정함이 확인되었다. 분류군별로는 서해안 갯벌에 도요·물떼새류, 남해안 담수·기수역에 수면성 오리류, 동해안에는 갈매기류 중심의 군집이 형성되었다. 또한 조사 지역의 71.43% (25개소)에서 국제적 중요 지역(Internationally Important Site, IIS) 기준을 충족하였으며, 총 36종(그 중 도요·물떼새류 22종)이 확인되어 국내 연안습지가 EAAF (East Asian–Australasian Flyway) 상에서 높은 생태적 중요성을 지니는 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구에서 확인된 공간적 군집 특성은 향후 권역·해역 수준의 바닷새 서식지 네트워크 보전 전략 수립 시 군집 및 서식지 단위 접근이 고려될 필요가 있음을 제안한다.
-
Community Structure and Spatial Distribution of Coastal Birds Observed at 35 Major Coastal Wetlands in Korea from 2016 to 2024
-
Review
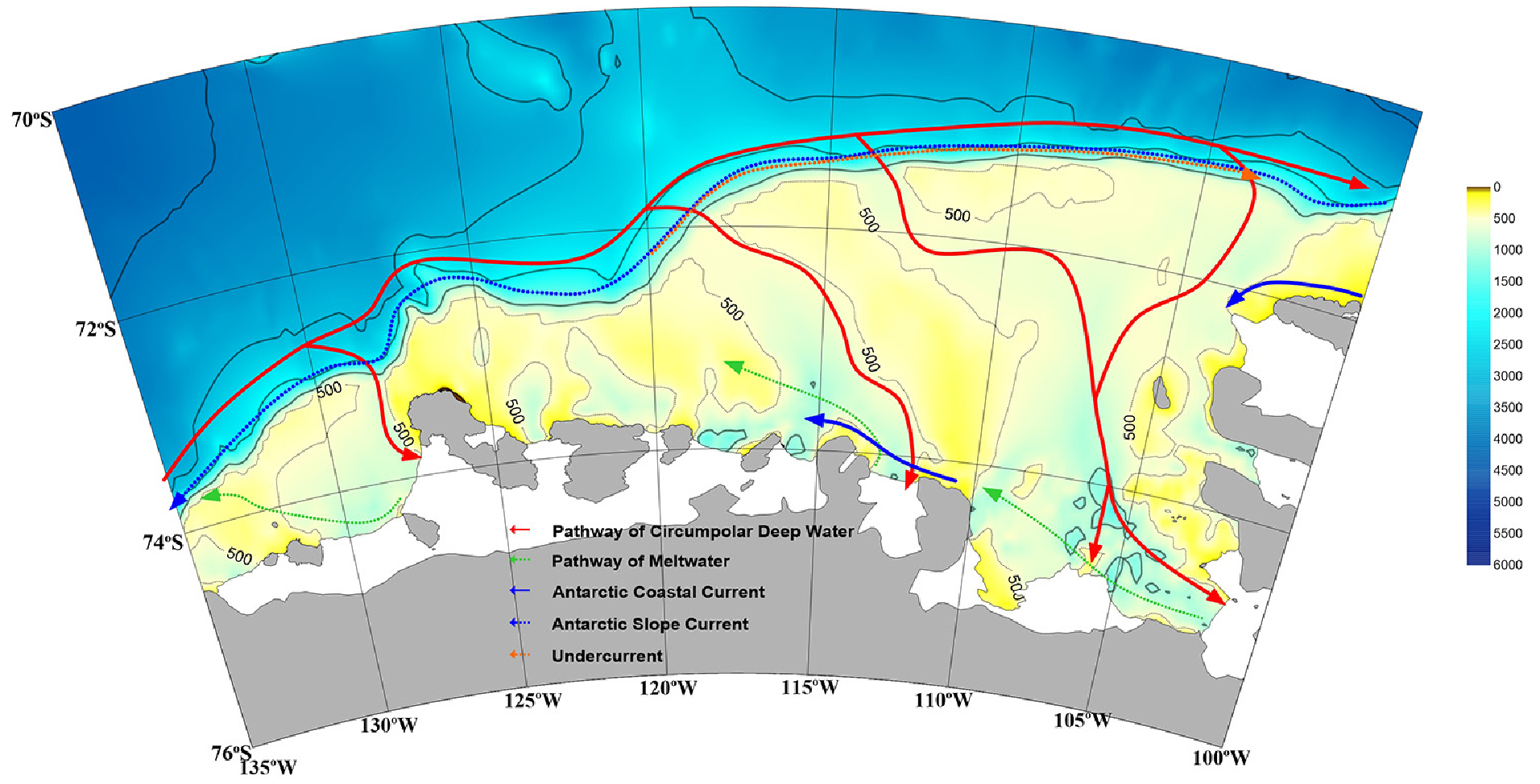
-
A Review of Oceanic Variability in the Amundsen Sea, West Antarctica: Implications of Climate Change
기후변화에 따른 서남극 아문젠해 해양 변동성에 대한 고찰
-
TAE-WAN KIM
김태완
- This study presents a comprehensive review of recent oceanic environmental changes and the variability of ice-shelf basal melting in the Amundsen Sea, …
본 연구는 최근 수십 년간 기후변화에 따른 서남극 아문젠해의 해양 환경 변화와 빙붕 기저 융해의 변동성을 종합적으로 고찰하였다. 아문젠해는 깊은 해저 골 …
- This study presents a comprehensive review of recent oceanic environmental changes and the variability of ice-shelf basal melting in the Amundsen Sea, West Antarctica, driven by climate change. Owing to its deep trough topography and the persistent influence of the Amundsen Sea Low, the Amundsen Sea is particularly vulnerable to the intrusion of Circumpolar Deep Water onto the continental shelf, resulting in the most rapid rates of ice-shelf melting and glacier retreat worldwide, especially at Pine Island Glacier and Thwaites Glacier. The regional water-mass structure is characterized by Antarctic Surface Water, Winter Water, and Modified Circumpolar Deep Water, and variability in the volume, temperature, and salinity of Circumpolar Deep Water directly regulates ice-shelf basal melting. Understanding the mechanisms of oceanic variability in the Amundsen Sea is therefore essential for reducing uncertainties in projections of West Antarctic Ice Sheet instability and its contribution to global sea-level rise. This variability is not governed by a simple warming trend but is strongly modulated by atmosphere-ocean-sea ice interactions, including wind-driven surface stress and curl associated with sea ice, as well as remote climate modes such as the Southern Annular Mode and El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Therefore, future research should prioritize sustained long-term observations and high-resolution coupled modeling to elucidate the interplay between large-scale climate modes and anthropogenic forcing. By synthesizing the current state of knowledge through an extensive literature review, this study provides a critical foundation for advancing future research on Antarctic and global climate change.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 최근 수십 년간 기후변화에 따른 서남극 아문젠해의 해양 환경 변화와 빙붕 기저 융해의 변동성을 종합적으로 고찰하였다. 아문젠해는 깊은 해저 골 지형과 상시적인 아문젠해 저기압 등 특수한 지역적 조건으로 인해 환남극 심층수의 대륙붕 유입이 용이하며, 이로 인해 파인아일랜드 빙하와 쓰웨이트 빙하에서 전 지구적으로 가장 빠른 융해와 후퇴가 진행되고 있다. 아문젠해 수괴 구조는 남극 표층수, 겨울수, 변형된 환남극 심층수로 특징지어지며, 특히 환남극 심층수의 부피 및 수온·염분의 변동은 빙붕 기저 용해를 직접적으로 조절한다. 따라서 아문젠해 해양 변동 메커니즘에 대한 이해는 서남극 빙상의 불안정성 및 전 지구 해수면 상승 예측의 불확실성을 줄이기 위해 필수적이다. 그리고 이러한 변동성은 단순한 온난화 추세가 아니라, 대기-해양 상호작용, 해빙-바람 응력 컬(curl), 그리고 남반구 환형모드, 엘니뇨-남방진동과 같은 원격 기후 모드의 영향에 의해 크게 좌우된다. 그러므로 향후 장기 관측과 고해상도 결합 모델을 통한 정밀 분석이 요구되며, 이를 통해 원격 기후 모드와 인위적 강제력의 상호작용을 규명하는 연구가 필요하다. 본 연구는 아문젠해의 해양 변동성에 대한 문헌 고찰을 바탕으로 현 단계의 이해를 종합적으로 정리함으로써, 향후 남극 및 전 지구 기후변화 연구에 중요한 기초자료를 제공한다.
-
A Review of Oceanic Variability in the Amundsen Sea, West Antarctica: Implications of Climate Change
-
Review
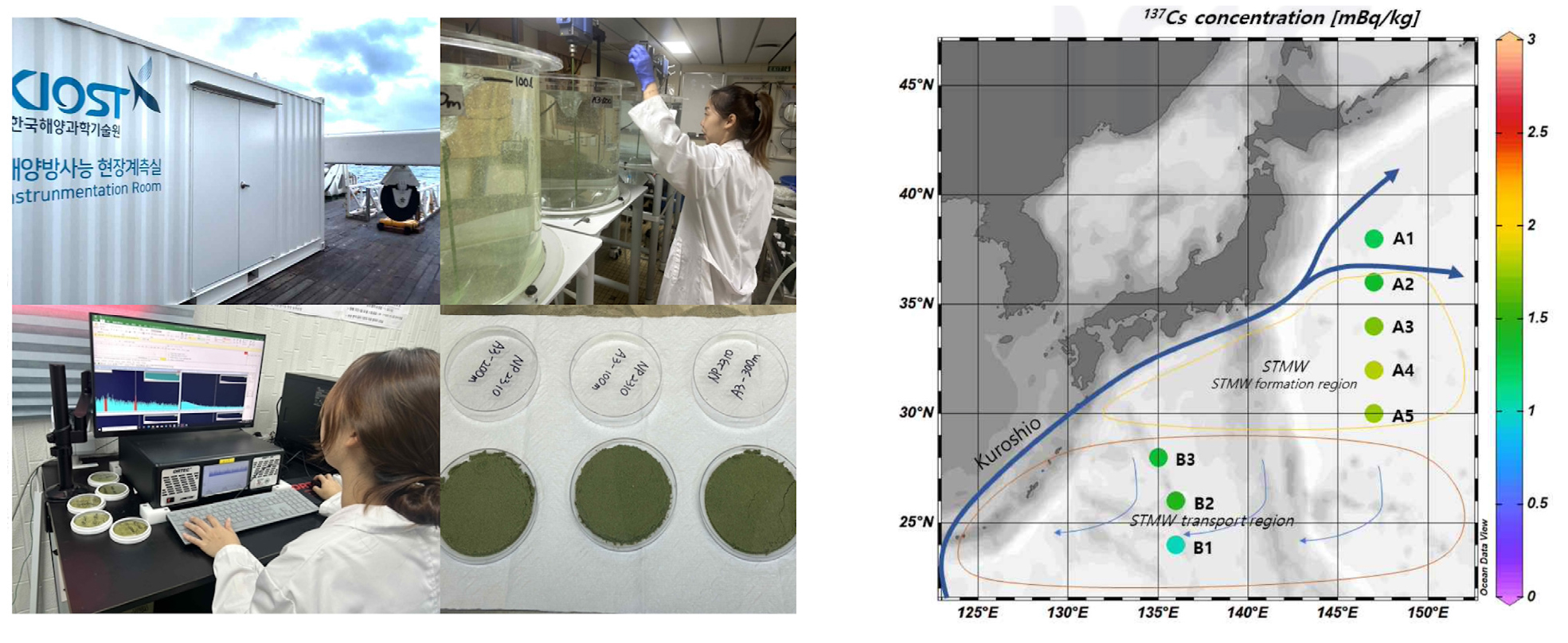
-
Current Status and Trends on Artificial Radionuclide Studies in the Korean Marine Environment
국내 해양환경 인공방사능 연구 동향
-
HEEJUN HAN, JUNHYEONG SEO, JAEEUN LEE, JIHYE SHIN, HYUNMI LEE AND INTAE KIM
한희준, 서준형, 이재은, 신지혜, 이현미, 김인태
- Marine radionuclide research in Korean seas has been continuously conducted in response to various events starting with the disposal of radioactive waste …
한국 해역에서의 해양 방사능 조사는 구소련(러시아)의 동해 핵폐기물 투기를 시작으로 핵실험 기원의 방사성 핵종, 원자력 발전소 방출, 그리고 2011년 후쿠시마 원전 사고 …
- Marine radionuclide research in Korean seas has been continuously conducted in response to various events starting with the disposal of radioactive waste in the East Sea by the former Soviet Union (now Russia) followed by the fallout from nuclear weapon testing, releases from nuclear power plants, and the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident in 2011 together with the discharge of treated radioactive wastewater in 2023. Since the Fukushima accident, extensive studies have been carried out in coastal waters for the direct and indirect inputs of radionuclides into the ocean including their transport pathways in the surrounding seas of Korea and their spatial and temporal distributions. These efforts have also brought increasing attention to the potential impacts on marine environments and biological systems. In addition, more than 300 nuclear power plants are currently planned and/or under construction in the seas surrounding the Korean peninsula including South Korea, Japan, and China, which raises public concern over nuclear safety in the northwestern Pacific region. Also, the Japanese government has released treated wastewater from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant into the ocean on several occasions and plans to continue these discharges over the next 30 years. These actions have drawn significant domestic and international attention and concern regarding their potential impacts on the marine environment. Recently, the scope of radionuclide research has expanded to investigate the long-term behavior, bioaccumulation, and biogeochemical cycling of radionuclides in seawater, marine sediments, and both benthic and marine organisms. Such studies provide essential scientific backgrounds for (1) protecting public health, (2) ensuring the stability of marine ecosystems, and (3) managing the radioactive safety of coastal seafood. Marine radioactivity has emerged as a significantly important issue that extends beyond environmental concerns to one requiring international cooperation and transparent data sharing. Thus, it is crucial to establish a real-time monitoring and science-based early warning systems. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of recent developments in marine radionuclide research conducted in Korean coastal waters following the Fukushima accident. This study also highlights recent trend and emphasizes the urgent need to establish a rapid detection and monitoring framework to support sustainable and responsive marine radiological surveillance in the future.
- COLLAPSE
한국 해역에서의 해양 방사능 조사는 구소련(러시아)의 동해 핵폐기물 투기를 시작으로 핵실험 기원의 방사성 핵종, 원자력 발전소 방출, 그리고 2011년 후쿠시마 원전 사고 및 2023년 후쿠시마 오염수 방류에 이르기까지 다양한 요인에 의해 지속적으로 수행되어 왔다. 특히 후쿠시마 원전 사고 이후 방사성 세슘(Cs-134, 137)을 비롯한 다양한 방사성 핵종의 해양과 대기, 그리고 한반도 주변 해역으로의 직, 간접적 유입 및 다양한 경로를 통한 영향과 그 분포 변화에 대한 연구가 활발히 진행되었으며 해양 환경 및 생물에 미치는 영향에 대한 관심도 크게 증가하였다. 또한, 한반도 주변 해역에는 한국, 일본, 중국을 포함한 300기 이상의 원자력 발전소 건설이 계획되고 있어 북서태평양 해역의 핵안전성에 대한 국민적 관심이 높아지고 있으며 최근 일본 정부는 후쿠시마 오염수를 해양으로 여러 차례 방류하였고 향후 30년에 걸쳐 해양 방류할 계획이다. 이러한 오염수의 해양 방류는 국내외적으로 우려와 관심을 불러일으키고 있다. 최근에는 해수 뿐만 아니라 해양 퇴적물, 저서생물, 어류 등에 축적된 방사성 핵종의 장기적인 거동과 생물학적 농축, 생지화학적 순환 과정에 대한 연구가 확대되고 있다. 이러한 연구는 국민 건강 보호는 물론 해양 생태계의 안정성 확보와 연안 수산물의 방사능오염 안전 관리를 위한 필수적인 과학적 기반을 제공한다. 또한 해양 방사능은 단순한 환경 이슈를 넘어 국제적 협력과 정보 공유가 요구되는 중요한 분야로 실시간 감시 체계의 구축과 과학 기반의 조기 대응 시스템 마련이 시급하다. 본 논문에서는 후쿠시마 원전 사고 이후 국내해에서 수행된 해양환경 방사능 관련 연구 결과와 최근 연구 동향을 종합적으로 소개하고 해양방사능 신속탐지 체계 구축의 필요성 등 향후 지속 가능한 감시 및 대응 체계 구축을 위한 방향성을 제시하고자 한다.
-
Current Status and Trends on Artificial Radionuclide Studies in the Korean Marine Environment
-
Review
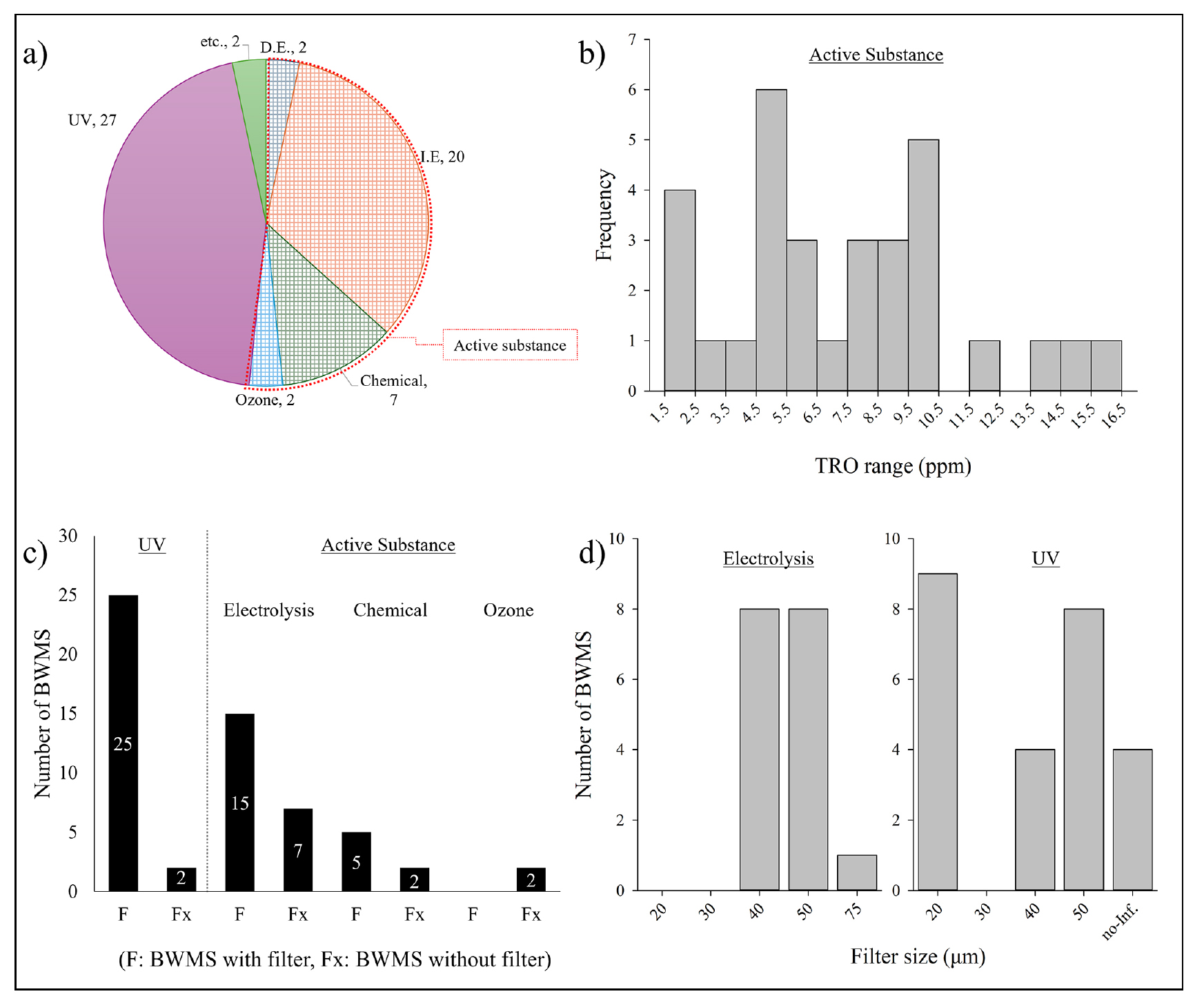
-
Regulatory Trends and Future Outlook in Ballast Water Management: A Comparative Perspective on IMO and U.S. Approaches
선박평형수 관리제도의 국제적 변화와 전망: 국제해사기구와 미국의 제도 동향 중심으로
-
PUNG-GUK JANG, WOO-JIN LEE AND KYOUNGSOON SHIN
장풍국, 이우진, 신경순
- The International Maritime Organization (IMO) adopted the Ballast Water Management Convention in 2004 to prevent the spread of invasive species via ballast …
국제해사기구(IMO)는 선박평형수를 통한 외래종 유입을 방지하기 위해 2004년 선박평형수관리협약을 채택하였고, 동 협약은 2017년에 발효하였다. 현재 국제해사기구는 협약 개정을 2026년까지 완료하고, 2028년부터 시행할 …
- The International Maritime Organization (IMO) adopted the Ballast Water Management Convention in 2004 to prevent the spread of invasive species via ballast water, with the Convention entering into force in 2017. A revision is planned for completion in 2026, with implementation scheduled for 2028. In parallel, the United States initiated ballast water regulation through the Vessel General Permit (VGP) in 2008 and later enacted the Vessel Incidental Discharge Act (VIDA) in 2018. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued final regulations in 2024, and the U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) plans to finalize implementation rules by 2026 and begin enforcement in 2027. IMO’s Experience Building Phase revealed that approximately 15% of surveyed vessels failed to meet the D-2 standard of ballast water discharge, mainly due to poor BWMS maintenance, inadequate performance verification, and insufficient crew training. Concerns over disinfection by-products (DBPs) were also raised. The upcoming Convention revision is expected to address these issues. The United States also aims to unify previously varying state-level discharge standards under a national standard through VIDA, and to establish a system that enables the timely strengthening of discharge standards in response to advancements in BWMS technology. This study analyzes recent international developments and regulatory shifts to inform policymaking and industrial strategy, with implications for improving the effectiveness of ballast water management and protecting marine ecosystems.
- COLLAPSE
국제해사기구(IMO)는 선박평형수를 통한 외래종 유입을 방지하기 위해 2004년 선박평형수관리협약을 채택하였고, 동 협약은 2017년에 발효하였다. 현재 국제해사기구는 협약 개정을 2026년까지 완료하고, 2028년부터 시행할 계획이다. 미국은 2008년 선박일반허가(VGP)를 통해 선박평형수 규제를 시작하였다. 2018년 선박부수배출법(Vessel Incidental Discharge Act, VIDA) 제정 이후 미국 환경보호청(EPA)은 2024년에 최종 규정을 발표하였고, 해당 규정은 같은 해에 발효되었다. 미국 해안경비대(USCG)는 이를 바탕으로 2026년까지 시행규칙을 확정하고, 2027년부터 본격 시행할 예정이다. 국제해사기구는 2017년부터 경험축적기(EBP)를 통해 수집한 선박평형수관리설비(BWMS) 운전자료를 분석하였다. 그 결과 조사 선박의 약 15%가 배출수 기준(D-2 기준)을 충족하지 못하였으며, 그 주요 원인은 장비의 유지관리 미흡, 성능 검증 부족, 선원 교육 미비 등이었다. 아울러 소독부산물(DBPs)에 대한 우려도 제기되어, 향후 협약 개정을 통해 이에 대한 관리 방안을 마련할 예정이다. 미국 또한 선박부수배출법을 통해 주마다 다른 배출수 기준을 국가 표준으로 통일하고, 장비 기술 발달에 따라 배출수 기준을 신속히 강화할 수 있는 체계를 구축하고자 한다. 본 논문은 이러한 국제적 동향과 제도 변화 추이를 분석하여, 정책 수립과 산업계 전략 마련에 기초자료를 제공하고, 선박평형수 관리의 실효성과 해양환경 보호에 대한 시사점을 도출하고자 한다.
-
Regulatory Trends and Future Outlook in Ballast Water Management: A Comparative Perspective on IMO and U.S. Approaches
-
Review
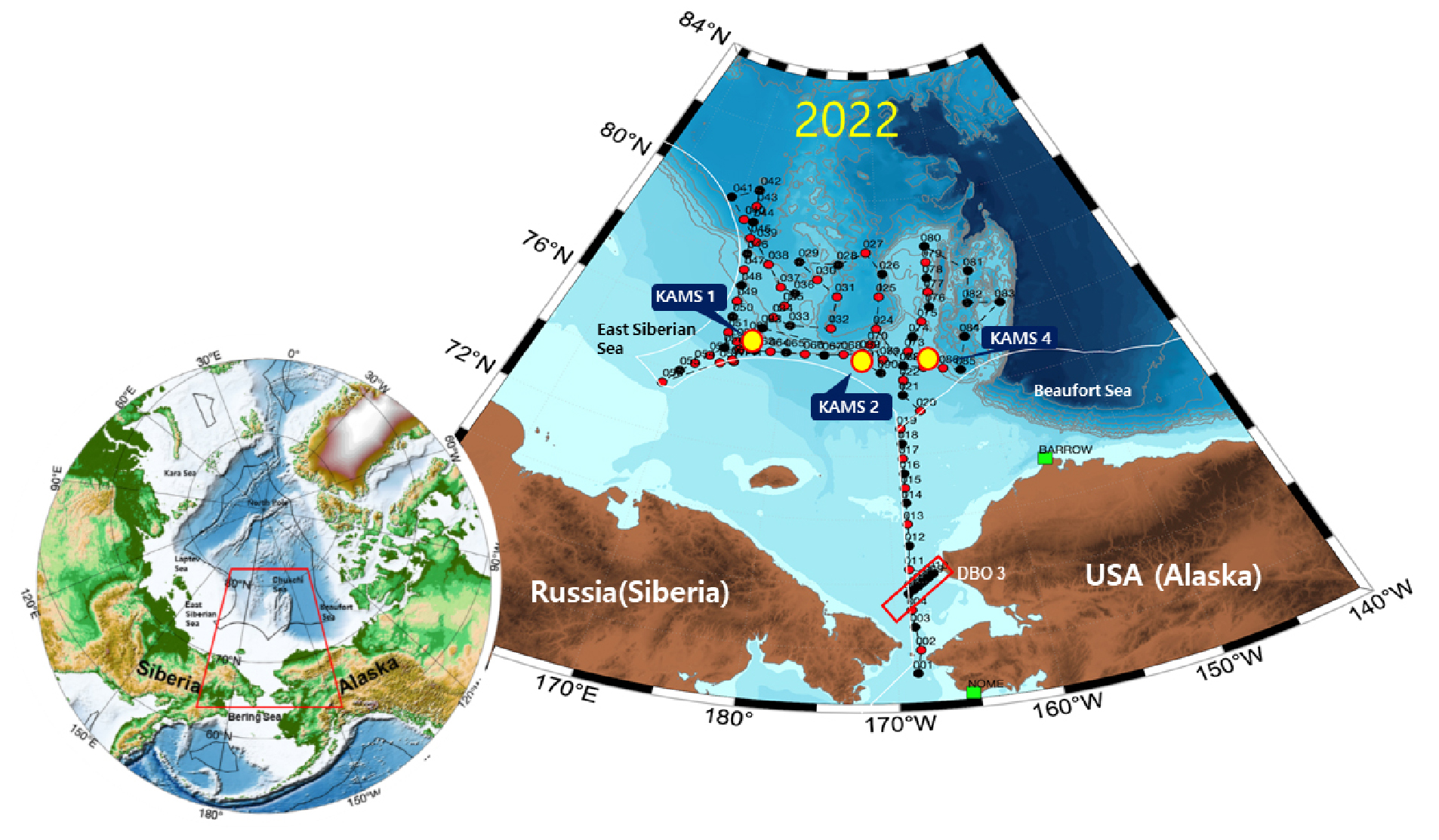
-
Environmental and Ecosystem Changes in the Western Arctic Ocean: A Research Overview
서북극해 해양 환경 및 생태계 변화 연구의 종합적 고찰
-
EUN JIN YANG
양은진
- The Arctic is experiencing the fastest rate of warming on Earth, leading to the rapid disappearance of sea ice and causing profound …
현재 북극은 전 지구에서 가장 빠른 속도로 온난화가 진행되면서 해빙이 급속히 소멸하고 있으며, 이는 기후 시스템과 해양환경, 생태계 전반에 중대한 영향을 미치고 …
- The Arctic is experiencing the fastest rate of warming on Earth, leading to the rapid disappearance of sea ice and causing profound impacts on the global climate system, marine environments, and ecosystems. These changes are not merely environmental issues but complex challenges closely linked to climate change, fisheries, Arctic shipping route, resource development, and geopolitics, all of which directly affect global climate stability. This review synthesizes environmental and ecosystem changes in the western Arctic Ocean using multidisciplinary observations from the IBRV ARAON, including long-term field surveys, moorings, sediment traps, eDNA analyses, satellite data, and numerical modeling. The study provides the first evidence that Atlantification has expanded into the East Siberian region, identifying the intrusion of Atlantic-origin water as a key process that can accelerate sea-ice loss. Phytoplankton communities are shifting from diatom-dominated to small flagellate-dominated structures, and both under-ice blooms and subsurface chlorophyll maxima were found to contribute substantially to primary production. Under-ice ecosystems were also shown to play an important role in regulating carbon fluxes. In addition, previously unrecognized biogeochemical anomalies including low-oxygen and highly acidified water masses were identified for the first time in the study. This study demonstrate that increased Atlantic water inflow, enhanced freshwater inputs, and sea-ice decline are jointly intensifying ocean acidification in this study area. Overall, the findings indicate that the western Arctic Ocean is undergoing a rapid transitional phase in which its physical, chemical, and ecological systems are being transformed simultaneously. Future research should focus on advancing long-term Arctic monitoring systems, strengthening international collaborations, and enhancing data interoperability to establish a robust scientific foundation for prediction and management. Furthermore, intensive year-round observations utilizing Korea’s next-generation ice-breaking research vessel will provide critical support for sustainable Arctic Ocean governance and contribute to global climate-change mitigation efforts.
- COLLAPSE
현재 북극은 전 지구에서 가장 빠른 속도로 온난화가 진행되면서 해빙이 급속히 소멸하고 있으며, 이는 기후 시스템과 해양환경, 생태계 전반에 중대한 영향을 미치고 있다. 이러한 변화는 단순한 환경 문제가 아니라 기후변화, 수산자원, 북극항로, 자원개발, 국제 지정학 등과 밀접하게 연관된 복합적 이슈로서, 전 지구 기후 안정성에 직접적인 영향을 미친다. 본 종설 논문은 쇄빙연구선 아라온을 활용한 서북극해 장기 현장관측, 해양계류장비, 퇴적물 트랩, eDNA 분석, 위성자료, 모델링 등 다중자료를 기반으로 북극 온난화가 초래한 서북극해의 해양환경‧생태계 변화를 통합적으로 정리하였다. 연구를 통해 북극해의 대서양화가 서북극해 동시베리아까지 확장되었으며, 대서양수 확장이 해빙소멸을 가속화할수 있는 핵심 메커니즘임을 세계 최초로 확인하였다. 서북극해 식물플랑크톤은 규조류 중심에서 소형 편모조류 중심 구조로 전환되고 있었으며, 해빙하 대번성과 엽록소 최대층이 실제 일차 생산에 크게 기여함을 규명하였고, 해빙하 생태계가 북극해 탄소플럭스에 중요한 역할을 함을 제시하였다. 또한 조사해역에서 저산소‧고산성화 수괴 등 새로운 생지화학적 이상 현상을 세계 최초로 규명하였으며, 대서양수 유입‧담수화‧해빙 감소 변화가 복합적으로 작용하여 서북극해 산성화가 빠르게 심화되고 있음을 확인하였다. 이러한 결과는 북극해가 물리‧화학‧생태계가 동시에 변화하는 전환기에 있음을 보여주고 있다. 향후 연구는 북극해 장기 모니터링 체계의 고도화, 국제공동연구 강화, 데이터 상호운용성 확보를 통해 예측 기반을 확립하고, 2029년 건조 예정인 차세대 쇄빙연구선을 활용한 집중 탐사를 통해 지속가능한 북극해 관리와 기후변화 대응을 선도하는 과학적 기반을 마련할 것이다.
-
Environmental and Ecosystem Changes in the Western Arctic Ocean: A Research Overview
-
Review
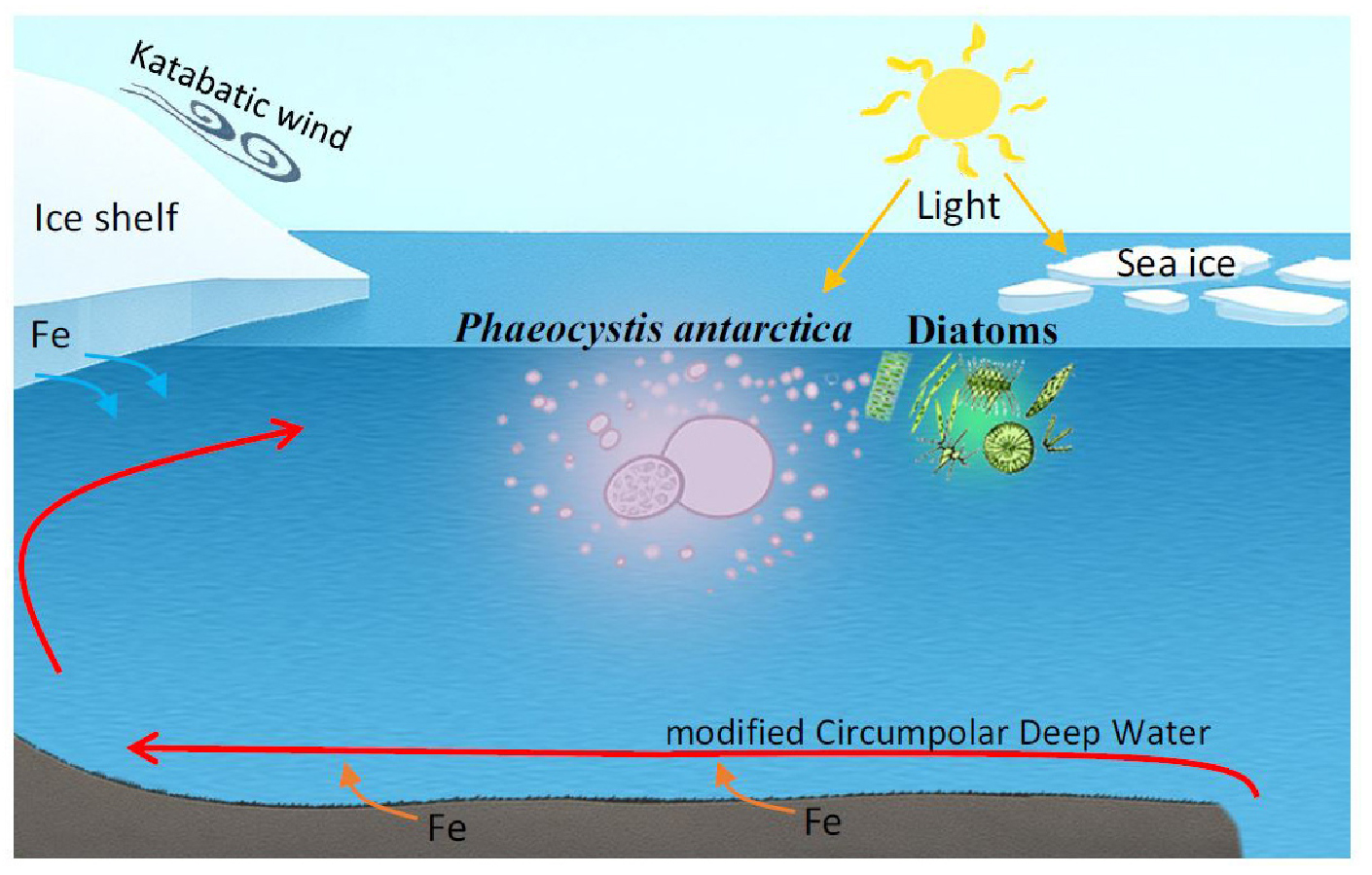
-
Phytoplankton Ecology in the Amundsen Sea, West Antarctica
서남극 아문젠해 식물플랑크톤 군집 생태 연구
-
YOUNGJU LEE
이영주
- The Amundsen Sea in West Antarctica is one of the most rapidly warming regions on Earth, characterized by the rapid thinning of …
서남극 아문젠해는 지구상에서 가장 급격한 온난화가 진행되는 해역 중 하나로 남극에서도 빙붕이 가장 빠르게 녹고있는 동시에 생산성이 높은 연안으로 잘 알려져 있다. …
- The Amundsen Sea in West Antarctica is one of the most rapidly warming regions on Earth, characterized by the rapid thinning of ice shelves and a highly productive coastal ecosystem. However, scientific investigation of this region has been limited due to its inaccessibility and geographic isolation. Since the discovery of the Amundsen Sea Polynya—one of the most productive coastal polynyas in Antarctica—through satellite observations in the early 2000s, the region has attracted substantial international attention and has become the focus of numerous research expeditions. In particular, the Korean icebreaker R/V Araon has conducted multi-year expeditions since 2010, contributing significantly to the understanding of phytoplankton community structure, biomass, primary production, physiological characteristics, and their seasonal and interannual variability. The biomass and community structure of phytoplankton in the Amundsen Sea responded sensitively to changes in the physicochemical environment, and these variations directly impacted biogeochemical cycles and food web structures. This underscores the importance of further research to elucidate the role of phytoplankton as a regulator of ecosystem changes and the carbon cycle under accelerating ocean warming.
- COLLAPSE
서남극 아문젠해는 지구상에서 가장 급격한 온난화가 진행되는 해역 중 하나로 남극에서도 빙붕이 가장 빠르게 녹고있는 동시에 생산성이 높은 연안으로 잘 알려져 있다. 하지만 오랜 기간 동안 접근의 어려움과 지리적 고립으로 인하여 연구의 사각지대에 놓여 있었다. 2000년대 초반 위성 데이터를 통하여 남극 연안에서 가장 일차생산이 높은 아문젠해 폴리냐의 존재가 밝혀진 후 국제적인 관심과 수 많은 탐사가 이어져 왔다. 특히 대한민국의 쇄빙연구선 아라온호는 2010년부터 다년간에 걸친 탐사를 수행하였다. 이 탐사를 통해 아문젠해의 식물플랑크톤 군집 분포, 생물량, 일차생산, 생리 특성이 밝혀졌으며, 계절적, 경년 변동 특성을 이해하는 데에 중요한 역할을 하였다. 아문젠해 식물플랑크톤의 생물량과 군집구조는 해양의 물리, 화학적 환경 변화에 민감하게 반응하였고, 이러한 일차생산자의 변화는 생지화학 순환과 먹이망 구조에 직접적인 영향을 미쳤다. 이는 가속화되는 온난화 속에서 아문젠해의 생태계 변화와 탄소 순환 조절자로서 식물플랑크톤의 역할을 규명하기 위한 후속 연구의 중요성을 강조한다.
-
Phytoplankton Ecology in the Amundsen Sea, West Antarctica
-
Newsletter

-
The Korean Society of Oceanography Newsletter
한국해양학회 소식지
-
2025.11
2025. 4호
-
The Korean Society of Oceanography Newsletter
Journal Informaiton
 The Sea Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography
The Sea Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 The Sea Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography
The Sea Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography











